Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Condition Basics
What is gastroesophageal reflux disease?
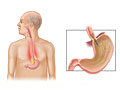
Reflux, Opens dialog means that stomach acid and juices flow from the stomach back up into the esophagus, the tube that connects the throat to the stomach. This causes heartburn or regurgitation. Regurgitation happens when food and liquid back up from the stomach into the esophagus and mouth. When you have heartburn or regurgitation that bother you often, it is called gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD. This can also cause pain and inflammation in your esophagus (esophagitis). You may also hear GERD called acid reflux.
Eating too much close to bedtime or before lying down sometimes can cause symptoms. But having heartburn or regurgitation from time to time doesn't mean that you have GERD. With GERD, the reflux and heartburn last longer and happen more often.
What causes it?
Normally when you swallow food, it travels down the esophagus. A valve opens to let the food pass into the stomach, and then the valve closes. With GERD, the valve doesn't close tightly enough. Stomach acid and juices from the stomach flow back up (reflux) into the esophagus.
What are the symptoms of GERD?
The main symptoms of GERD are heartburn and regurgitation. Heartburn feels like burning or pain behind the breastbone. Regurgitation happens when food and liquid back up from the stomach into the esophagus and mouth. It is common to have symptoms when you're trying to sleep.
How is it diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, such as whether you often have heartburn. If you do, your doctor may recommend a medicine that reduces or blocks stomach acid to see if it helps. Some people need tests like an upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy or tests for acid in the esophagus.
How is GERD treated?
Treatment starts with changing your habits and taking over-the-counter medicines. For example, not eating for a few hours before bedtime may help. Try medicines such as antacids (like Tums) or H2 blockers (like Pepcid). If you don't get better, a doctor may suggest more testing or a change in medicine. Some people need surgery.
What can you do to reduce your symptoms?
Take your medicines as directed. These may include prescription or over-the-counter medicines. Eat several small meals a day. Avoid foods that make your GERD worse, like chocolate, mint, and spicy foods. After eating, wait 2 to 3 hours before lying down. For symptoms when you are trying to sleep, raise the head of your bed 6 to 8 inches.
Health Tools
Health Tools help you make wise health decisions or take action to improve your health.
Cause
GERD happens because of a problem with the ring of muscle at the end of the esophagus called the lower esophageal sphincter. It acts like a one-way valve between the esophagus and the stomach. When you swallow, the valve lets food pass into the stomach. With GERD, the valve doesn't close tightly enough. Stomach acid and juices flow back up (reflux) into the esophagus.
GERD usually happens when the valve relaxes at the wrong time and stays open too long. Some things may relax the valve so it doesn't close tightly or some foods and drinks can make GERD worse. These may include chocolate, mint, alcohol, pepper, spicy foods, high-fat foods, or drinks with caffeine in them, such as tea, coffee, colas, or energy drinks. If your symptoms are worse after you eat a certain food, you may want to stop eating it to see if your symptoms get better.
Other things can make stomach juices back up, such as:
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy.
- A weak lower esophageal sphincter.
- A hiatal hernia.
- Slow digestion.
- An overfull stomach.
- Being overweight or having obesity.
What Increases Your Risk
Things that increase your risk for symptoms of GERD may include:
- Smoking.
- Eating certain foods. These may include chocolate, mint, alcohol, pepper, spicy foods, high-fat foods, or drinks with caffeine in them, such as tea, coffee, colas, or energy drinks. If your symptoms are worse after you eat a certain food, you may want to stop eating it to see if your symptoms get better.
- Health conditions, such as:
- Being overweight or having obesity.
- Being pregnant. GERD is a common problem during pregnancy. Most of the time, symptoms get better after the baby is born.
- Having a hiatal hernia.
- Taking certain medicines. If you think that a medicine you take may be causing your GERD symptoms, talk to your doctor.
Learn more
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) During Pregnancy
- Hiatal Hernia
Prevention
You may be able to prevent GERD with lifestyle changes, such as eating healthy foods, not smoking, and staying at a weight that is healthy for you. Talk to your doctor if you need help losing weight.
Some medicines may cause GERD as a side effect. If any medicines you take seem to be the cause of your heartburn, talk with your doctor. Don't stop taking a prescription medicine until you talk with your doctor.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of GERD are:
- Heartburn. Heartburn is an uncomfortable feeling or burning pain behind the breastbone. It may occur after you eat, soon after you lie down, or when you bend forward. Some people have GERD without heartburn.
- Regurgitation. This happens when food and liquid back up from the stomach into the esophagus and mouth.
Other symptoms may include:
- Chest pain.
- Hoarseness.
- Trouble swallowing.
- A feeling that something is stuck in your throat.
- A cough.
- Having extra saliva.
- Nausea.
What Happens
GERD may cause irritation or inflammation in the esophagus, the tube that connects the throat to the stomach. This condition is called esophagitis, Opens dialog.
Mild GERD symptoms are an uncomfortable feeling of burning, warmth, heat, or pain just behind the breastbone. Some people have regurgitation, when food and liquid back up from the stomach into the esophagus and mouth. You may be able to treat these symptoms with over-the-counter medicines that reduce or block acid.
Advanced GERD can cause problems such as:
- Severe esophagitis, esophageal erosion, and ulcers.
- A narrowed esophagus.
- Barrett's esophagus, Opens dialog. With this, the cells that line the inside of the esophagus are replaced by cells like those that line the inside of the stomach and intestine.
- Respiratory problems. These include a cough that won't go away, asthma, pneumonia, and laryngitis.
- The speeding up of tooth decay. This is because stomach acid gets into the mouth and wears away tooth enamel.
Some people who have GERD may have a higher risk for cancer of the esophagus.
Learn more
When to Call a Doctor
The main symptom of GERD is an uncomfortable feeling of burning, warmth, heat, or pain just behind the breastbone. This feeling is often called heartburn. Sometimes heartburn can feel like the chest pain of a heart attack.
Call 911 or other emergency services immediately if:
- You have symptoms of a heart attack. These may include:
- Chest pain or pressure, or a strange feeling in the chest.
- Sweating.
- Shortness of breath.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Pain, pressure, or a strange feeling in the back, neck, jaw, or upper belly or in one or both shoulders or arms.
- Lightheadedness or sudden weakness.
- A fast or irregular heartbeat.
After you call 911, the operator may tell you to chew 1 adult-strength or 2 to 4 low-dose aspirin. Wait for an ambulance. Do not try to drive yourself.
Call your doctor now if you:
- Have new or worse belly pain.
- Vomit blood.
- Have bloody, black, or maroon-colored stools.
Call your doctor:
- If your GERD symptoms do not improve after 2 weeks of home treatment, are different or are getting worse, or are interfering with your usual activities.
- If food seems to catch in your throat or chest.
- If your symptoms occur with a lot of weight loss when you aren't trying to lose weight.
Watchful waiting
Watchful waiting, Opens dialog is a wait-and-see approach. If your heartburn is mild and happens only now and then, you may get relief by making lifestyle changes and taking nonprescription medicines that reduce or block acid.
Exams and Tests
To find out if you have GERD, your doctor will do a physical exam and ask you questions about your health. Your doctor may ask about your symptoms, such as whether you often have heartburn or regurgitation. If you do have heartburn or regurgitation often, your doctor may suggest a medicine that reduces or blocks stomach acid.
If your heartburn or regurgitation goes away after you take the medicine, you may not need any tests.
If you have tests, they may include:
- An upper gastrointestinal endoscopy.
- Esophageal tests.
- An upper-gastrointestinal X-ray series.
Learn more
Treatment Overview
Treatment aims to reduce reflux, prevent damage to your esophagus, and prevent problems caused by GERD.
For mild symptoms, try over-the-counter medicines such as:
- Antacids (like Tums).
- H2 blockers (like Pepcid).
- Proton pump inhibitors (like Prilosec).
Lifestyle changes can help. You can:
- Stay at a weight that's healthy for you. Extra weight puts a lot of pressure on the valve between the stomach and esophagus. Losing even a few pounds can help. Talk to your doctor if you need help losing weight.
- Change your eating habits:
- Try to eat several small meals instead of two or three large meals.
- Wait 2 to 3 hours after eating before lying down. Snacking close to bedtime can make your symptoms worse.
- Avoid foods that make your symptoms worse. These may include chocolate, mint, alcohol, pepper, spicy foods, high-fat foods, or drinks with caffeine in them, such as tea, coffee, colas, or energy drinks. If your symptoms are worse after you eat a certain food, you may want to stop eating it to see if your symptoms get better.
- Try to quit smoking or chewing tobacco, or cut back as much as you can. If you need help quitting, talk to your doctor about quit-tobacco programs and medicines. These can increase your chances of quitting for good.
- If you have GERD symptoms while trying to sleep, raise the head of your bed 6 to 8 inches by putting the frame on blocks or placing a foam wedge under the head of your mattress. (Adding extra pillows does not work.)
- Do not wear tight clothing around your middle.
If symptoms persist, possible next steps include a change in medicine or testing. Your doctor may recommend surgery to strengthen the valve between your esophagus and stomach.
Learn more
Medicines
Antacids, H2 blockers, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are usually tried first to treat GERD and its symptoms. These can be either prescription or over-the-counter.
Medicines can:
- Relieve symptoms (heartburn, Opens dialog, regurgitation, Opens dialog, or pain).
- Allow the esophagus to heal.
- Prevent problems caused by GERD.
You may take:
- Antacids. These include Mylanta and Tums. Antacids neutralize stomach acid and relieve heartburn. If you want to take medicine only when your symptoms bother you, antacids are a good choice.
- Acid reducers, such as:
- H2 blockers. These include cimetidine (Tagamet) and famotidine (Pepcid). H2 blockers reduce the amount of acid in the stomach. Most are sold in both over-the-counter and prescription strength.
- PPIs. These include lansoprazole (Prevacid) and omeprazole (Prilosec). PPIs reduce the amount of acid in the stomach. Some are available over-the-counter.
If your daily medicine doesn't control your GERD symptoms, talk with your doctor. You may need to try a different medicine.
Learn more
Surgery
Surgery and other procedures can treat GERD. They're usually done when medicines haven't worked well enough. Most of the procedures work by strengthening the valve (lower esophageal sphincter) between the esophagus and the stomach. This helps keep acid from backing up into the esophagus.
Some examples are:
- Fundoplication. With this surgery, the stomach is wrapped around the esophagus to strengthen the valve. This is usually done using surgery, but sometimes it is done using endoscopy.
- Magnetic sphincter augmentation (MSA). A string of magnetic beads is wrapped around the valve.
- Stretta procedure. This uses radio waves to tighten the valve.
- Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. This might be used if you have obesity.
Procedures for GERD can cause problems with swallowing, burping, and extra gas. You may need other procedures to fix these problems.
Learn more
Related Information
Credits
Current as of: October 19, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: October 19, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com.
© 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.